Well, in the very extensive domain of diesel engines, hardly ever is it mentioned as to who keep them going: the humble diesel fuel pumps. These ultimate components play a great deal in the overall performance and efficiency of diesel engines whether heavy-duty trucks or small generators. Here, you’ll find an all-inclusive guide that speaks to mechanics of diesel fuel pumps, kinds of pumps, maintenance, troubleshooting advice, and more.
Understanding Diesel Fuel Pump
What is a Diesel Fuel Pump?
A diesel fuel pump is a device that transmits diesel fuel from a tank into the combustion chamber of an engine. Unlike gasoline engines, the configuration of diesel engines is relatively complicated because a need for diesel fuel delivery under very high pressure is necessary to guarantee proper atomization and combustion.
The pump can be categorized into two main types: mechanical and electrical.
- Mechanical Fuel Pumps: Often found in older diesel engines, these pumps rely on a diaphragm that is actuated by the engine’s motion. They are generally reliable and straightforward but can struggle with high fuel demands.
- Electrical Fuel Pumps: These are more common in modern diesel engines. They utilize an electric motor to create the pressure needed for fuel delivery. They can handle higher fuel flow rates and pressures, making them suitable for a variety of applications.
How Do Diesel Fuel Pump Work?
In fact, it’s great the way a diesel fuel pump works, so let me detail it out. The pump sucks in the fuel from the tank into itself through a filter that removes all impurities. Following the filtering process, the pump then enhances it by air pressure to be provided to the fuel injectors, which atomize the fuel for effective combustion.
Here’s a simplified step-by-step process:
- Fuel Intake: The pump draws fuel from the tank.
- Filtration: The fuel passes through a filter to eliminate contaminants.
- Pressurization: The pump pressurizes the fuel to a specific PSI (pounds per square inch) necessary for proper injection.
- Fuel Delivery: The pressurized fuel is sent to the injectors, where it’s atomized for combustion.
This process is vital for ensuring that your diesel engine runs smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal emissions.
Types of Diesel Fuel Pump
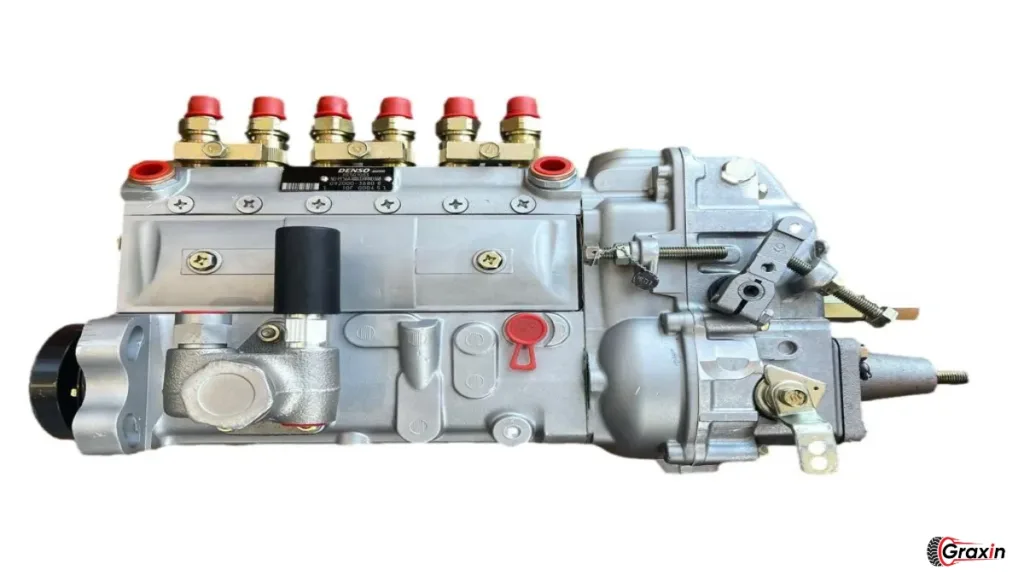
Mechanical Fuel Pumps
Mechanical fuel pumps are often located on the engine block and are driven by the engine’s motion. They have a relatively simple design but can face challenges, especially under high-demand situations.
Advantages of Mechanical Pumps:
- Simplicity: Easier to diagnose and repair.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than their electric counterparts.
- Reliability: Known for long-lasting performance.
Disadvantages of Mechanical Pumps:
- Limited Flow Rate: Struggles with high fuel demands.
- Wear and Tear: Mechanical components can wear out over time.
Electric Fuel Pumps
Electric fuel pumps can be found either inside the fuel tank (submersible) or outside of it. They are prevalent in newer diesel engines due to their ability to handle higher pressures and flow rates.
Advantages of Electric Pumps:
- High Flow Rate: Can deliver more fuel, making them suitable for performance engines.
- Versatility: Can be used in various applications.
- Less Noise: Generally quieter than mechanical pumps.
Disadvantages of Electric Pumps:
- Complexity: More components mean more potential points of failure.
- Cost: Typically more expensive upfront.
Common Rail Fuel Pumps
These pumps represent the cutting edge of diesel fuel delivery technology. They work by providing a constant high-pressure fuel supply to multiple injectors, improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
Advantages of Common Rail Systems:
- Improved Efficiency: Allows for multiple injections per cycle.
- Lower Emissions: Better atomization leads to cleaner combustion.
Disadvantages of Common Rail Systems:
- Costly Repairs: If something goes wrong, repairs can be expensive.
- Sensitive to Fuel Quality: Requires high-quality diesel to function effectively.
Maintaining Your Diesel Fuel Pump
Routine Maintenance Practices
Maintaining your diesel fuel pump is crucial for ensuring its longevity and efficiency. Here are some essential tips:
- Regular Fuel Filter Changes: Change your fuel filter regularly to prevent debris from damaging the pump. A clogged filter can lead to pump failure.
- Use Quality Fuel: Always fill your tank with high-quality diesel to minimize the risk of contaminants.
- Check for Leaks: Regularly inspect your fuel lines and pump for leaks, which can reduce efficiency and increase costs.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye (or ear) on how your engine is performing. Unusual sounds or performance issues can indicate a fuel pump problem.
- Check Electrical Connections: For electric pumps, ensure that all electrical connections are secure and corrosion-free.
Signs Your Diesel Fuel Pump Needs Attention
- Poor Engine Performance: If your engine is struggling to start or runs rough, it may be a sign of a failing fuel pump.
- Fuel Leaks: Notice any fuel puddles or smell of diesel? That’s a red flag.
- Strange Noises: Unusual noises, like whining or buzzing, can indicate issues with the pump.
- Warning Lights: If your dashboard warning lights come on, don’t ignore them; they could indicate a fuel delivery problem.
Troubleshooting Common Diesel Fuel Pump Issues

Diagnosing Fuel Pump Problems
If you suspect that your diesel fuel pump is malfunctioning, here’s a simple troubleshooting guide to help you out.
- Check Fuel Pressure: Use a pressure gauge to measure the fuel pressure at the pump. Compare your readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect Fuel Lines: Look for cracks or leaks in your fuel lines. Even a small crack can cause significant problems.
- Examine the Fuel Filter: If you haven’t changed your fuel filter in a while, it could be clogged, leading to pump strain.
- Electrical Checks: For electric pumps, use a multimeter to check voltage and continuity.
- Listen for Pump Operation: If you hear no sound from the pump when the ignition is turned on, it may be faulty.
Real-Life Example: A Truck Owner’s Dilemma
Think of Bob, truckdriver for many years. The day passes hauling his load across the country; the truck sputters. After some detective work he determines that the fuel filter was clogged and starving the pump. He returned to the road simply by replacing the filter but by doing so discovered the value of good maintenance.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, diesel fuel pumps are what give diesel engines their performance and efficiency. Knowing what kinds are used, what maintenance is needed, and how to trouble shoot them can be saved in the long run for time and money. Being a seasoned mechanic or just the casual diesel enthusiast, it makes all the difference when you have this knowledge at your fingertips.
Don’t let a fuel pump problem stall your plans; keep your diesel engine running smoothly with proactive care and attention!
FAQs
1. What are the signs of a failing diesel fuel pump?
Signs include poor engine performance, unusual noises, fuel leaks, and warning lights on the dashboard.
2. How often should I change my fuel filter?
It’s advisable to change your fuel filter every 10,000 to 15,000 miles, but consult your vehicle’s manual for specific recommendations.
3. Can I repair a diesel fuel pump myself?
While some minor repairs may be possible, it’s often best to consult a professional for significant issues.
4. What type of diesel fuel pump is best for my truck?
The best pump depends on your engine type and usage. Electric pumps are generally better for modern engines, while mechanical pumps can be reliable for older models.
5. How can I improve my diesel fuel pump’s lifespan?
Regular maintenance, using high-quality fuel, and monitoring for issues can significantly enhance your pump’s longevity.
Also Read: How Electric Car AC Works: Science Behind Cooling your car







